Updated by 10.02.2024
What Are Mobile Payments: Everything You Need to Know
Digital payment transactions are proliferating due to smartphone adoption, high-speed mobile data networks, and the growth of e-Commerce. 82% of Americans use mobile payments as they continue to get faster, cheaper, and more transparent.
Ideally, all businesses should offer mobile payment solutions to stay competitive and provide customers with the best possible service. This blog explains “what is mobile payment” and provides an overview of the different types of mobile systems and app recommendations, and, lastly, why your business should accept mobile payments.
What Is a Mobile Payment?
A mobile payment is a contactless way of paying that involves a mobile device such as a smartphone, a smartwatch, or a tablet. Such payments are conducted digitally, without a credit or debit card swiping through or being inserted into a point-of-sale device.
People use mobile payment systems to pay for goods or services, transfer money to another person or account, and pay bills. Payments are typically made using a mobile wallet – a digital account that stores payment information. Merchants use mobile payment readers to accept payments from customers.
Mobile Payment Solutions

Mobile payment solutions have become a gateway to other mobile financial services, such as mobile banking, insurance, credit/lending, and investment products. Furthermore, consumers have increasingly begun adopting cryptocurrency for payments, trading, savings, and investing.
Mobile Money
Mobile money services are a type of financial service that can be used without a traditional bank account. All that is required is a basic mobile phone. Customers register with a mobile money agent, who provides them with a virtual account – also known as a mobile wallet – connected to their phone number.
Customers can efficiently perform transactions with minimal physical contact using the SIM toolkit, SMS notifications, USSD, or even a mobile app.
The introduction of mobile payment methods such as these has drastically changed the financial sector in developing countries, giving individuals without access to traditional banking services a secure and convenient way to make financial transactions and increasing financial inclusion.
Electronic Money
Electronic money, or e-money, is a digital form of money stored electronically on a device or online. It can be used to make payments, transfer funds, and purchase goods and services. It differs from cash (fiat), issued by a central bank and typically stored physically, such as coins and paper bills. Examples of e-money include:
- Funds are stored in a mobile money account;
- A prepaid card;
- An online account like Paypal or Revolut.
Mobile Banking Services
M-banking is a way to use a mobile device to access banking and financial services offered by banks. Through m-banking, customers can view their bank account balance, carry out online transactions, move money, pay bills, and more without going to a physical bank.
M-banking, available through SMS, USSD, or an app, allows customers to access banking services anywhere. Additionally, it helps banks save operating costs and expand their customer base.
To use m-banking, customers must first download the bank’s app from the app store. They then need to register for the service by creating an account, which includes answering questions, selecting a username and password, and setting security preferences.
After that, they must create an MPIN to use when making a transaction. Once the bank verifies the information, the customer becomes a registered user and can make financial transactions through the mobile app.
Forms of Mobile Payments
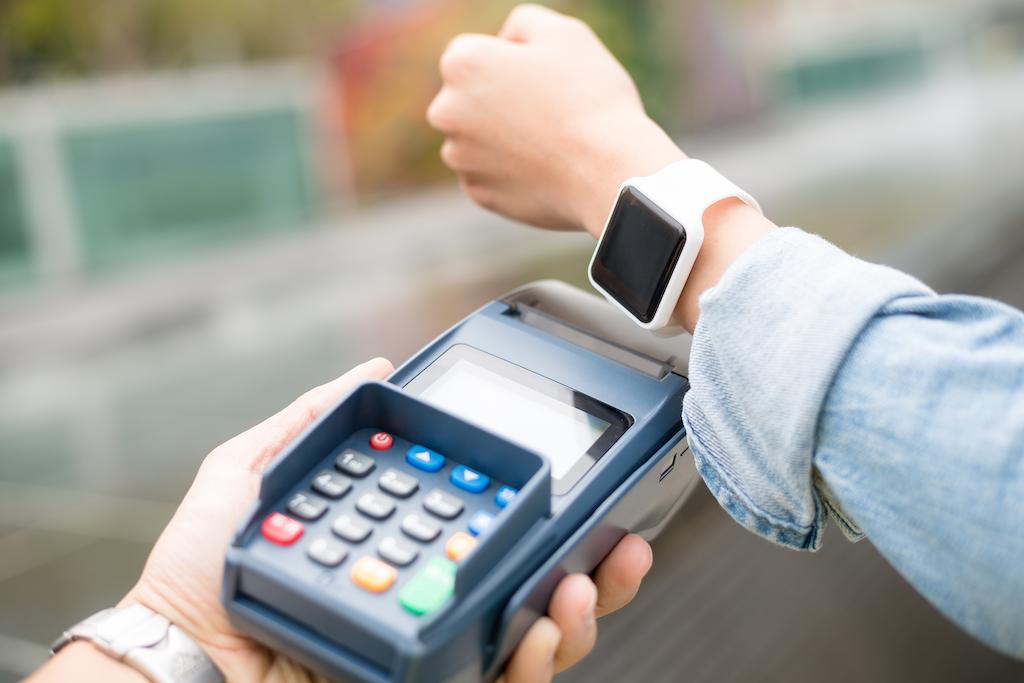

There are two forms of mobile payments: proximity payments and remote payments. Proximity payments are made at a close distance, usually at a point-of-sale (POS). On the other hand, remote payments are made online, such as when paying a bill, sending money to someone, or sending a remittance.
Proximity
With proximity payments, customers and merchants can communicate and transact using mobile payment technologies such as near-field communication (NFC), QR codes, and Bluetooth low energy (BLE). It allows customers to pay for goods and services without physically swiping a card or entering a PIN.
The merchant POS location may be attended (in-store) or unattended (self-check-out, vending machine). Both parties communicate and transact using a proximity mobile payment technology such as near field communication (NFC) mobile payment wallet.
Remote
Remote payments can be made through a fixed or mobile telecommunication network (internet), regardless of the customer’s location. This form of payment is convenient for merchants who don’t have a physical store or who sell digital items and services, such as SaaS companies.
5 Different Types of Mobile Payments
The different types of mobile payments and mobile payment technology make it easy for anyone with a smartphone and merchants to purchase and sell goods and services.
1. Mobile Wallet
A mobile wallet is an app or digital service that allows users to store and access their payment information, loyalty cards, and other digital assets on their mobile devices.
Each bank card stored in a mobile wallet is linked to a personal identification number, key, QR code, fingerprint, or facial recognition for secure transactions. Mobile wallets use near-field communication (NFC) to pay merchants.
NFC mobile payment technology utilizes radio frequencies to communicate securely between devices and transfer payment information to merchants’ point-of-service (POS) terminals. Typically, this is done by waving or holding an NFC-enabled device over the merchant’s NFC reader.
Mobile wallets are popular because they provide an easy, secure, and convenient way to manage financial and personal data.
2. Mobile Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
Peer-to-peer (P2P) payments, also known as person-to-person payments, are digital transactions between two individuals. This type of mobile banking allows for money to be directly transferred from one person’s bank account, debit card, credit card, checking account, or payment app to another person’s bank account or app.
3. SMS Payments
SMS or mobile payments are a form of payment that allows customers to pay for goods or services using a text message. This type of payment is especially popular with customers who do not have a credit card or do not want to use their credit card for certain purchases. Customers enter their phone numbers to authorize the payment and complete the transaction.
4. Mobile E-commerce

Mobile e-commerce (m-commerce) uses wireless handheld devices like cell phones and tablets to conduct commercial transactions online. It is a subset of e-commerce specifically designed to operate on mobile devices and allow users to access online stores and purchase products or services on the Internet.
5. Mobile Point of Sale (mPOS)
Mobile Point of Sale (mPOS) is a payment system that utilizes a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet to accept payments instead of traditional point-of-sale (POS) terminals. With mPOS, merchants can easily and securely accept credit and debit cards and other payment methods anywhere their customers are.
What Is NFC Mobile Payment?
NFC (Near Field Communication) payments are contactless payments that use an NFC-enabled device, such as a smartphone, to make payments at a point-of-sale terminal. To make an NFC mobile payment, you will need either a mobile wallet app or a contactless-enabled credit or debit card (you can check if your card is contactless-enabled here).
You will also need a payments reader, such as the Square contactless and chip reader, to accept contactless payments at your business. NFC can only transfer data between devices within a four-inch radius of each other.
This is why when purchasing with a mobile wallet, the user must hold the device close to the contactless payment reader to complete the transaction.NFC payments, including retail stores, restaurants, vending machines, and public transportation systems, can be used almost anywhere.
Contactless Cards
Other forms of mobile payments include contactless cards. They allow customers to make purchases without swiping or inserting the card into a reader. Instead, the customer holds the card, or a compatible device, such as a smartphone, near a contactless reader to make the payment. Contactless cards use near-field communication (NFC) technology to transmit payment information securely.
Apple Pay
Apple Pay is available to use on iPhone devices (version 6 or newer), as well as Apple Watch. To use Apple Pay, a customer must add any debit or credit card to the Wallet app on their device.
When they’re at a store that accepts Apple Pay, they just have to hold their iOS device over the payments reader and authenticate the payment with Touch ID, Face ID, or double-clicking the side button on their Apple Watch.
To accept Apple Pay as one of your mobile payment methods, you’ll need a Square reader enabled for NFC. Customers can pay for items online with the “Buy With Apple Pay” button on the checkout page. Additionally, you can accept Apple Pay through your app or website without a reader if you run an online store.
Google Pay
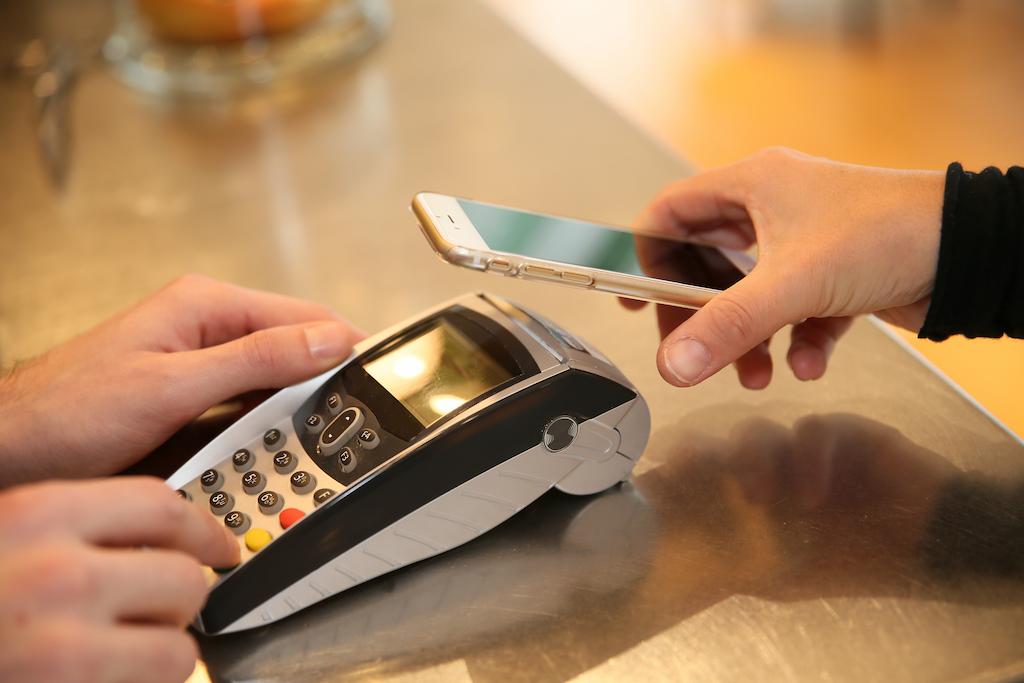

Google’s mobile wallet technology, Google Pay, is available on all NFC-enabled devices that run Android version 4.4 or later. To use Google Pay, a customer must open the app on their phone (which requires a secure lock screen) and complete the transaction by holding their device over the payments reader.
Samsung Pay
Samsung Pay allows users of certain Samsung Galaxy mobile devices to utilize their phone to pay almost everywhere they can use their Chase credit, debit, and/or Chase Liquid® cards. These select Samsung Galaxy devices come with Near Field Communication (NFC) which securely sends an encrypted version of a customer’s credit/debit card payment information to your terminal.
How Do Mobile Phone Payments Work?
Mobile payment services work as follows:
- When customers make payments with their mobile devices at a store, they need to hold their mobiles close to the NFC-enabled payments terminal.
- These types of payments are known as contactless payments since there is no physical contact between the device and the reader.
- Instead, the phone and the point of sale communicate through radio frequency. This process is quick and secure, as tokenization is used to protect your financial information.
Tokenization is a mobile payment technology that replaces bank account details with randomly generated numbers. For example, with Apple Pay, after a customer uploads their credit card information to their iPhone, Apple sends the details to the card’s issuing bank, who then replaces the details with a token. This token is programmed into their phone, making it impossible for fraudsters to clone bank account details.
Why Should You Use Mobile Payments?
Whether it’s an NFC mobile payment, QR code, or Bluetooth, there’s no doubt mobile payments eliminate a barrier to finalizing customer purchases. Here’s why your business would benefit from accepting mobile payments.
Convenience
Mobile payments are becoming the most practical payment method as people increasingly rely on their phones for everyday needs. Instead of visiting an ATM to pay someone back, individuals can now easily send an e-transfer through their bank’s app. Furthermore, there is no need to take out a wallet at the checkout counter; it only takes a simple phone tap.
Swiftness
Mobile payments via contactless technology are incredibly fast, taking just a second to process. This makes them even faster than credit card transactions and much quicker than a traditional swipe or EMV chip payments. For businesses with long checkout lines, contactless payments offer an attractive solution as they can help move the line faster, meaning more sales in a shorter period of time.
Security
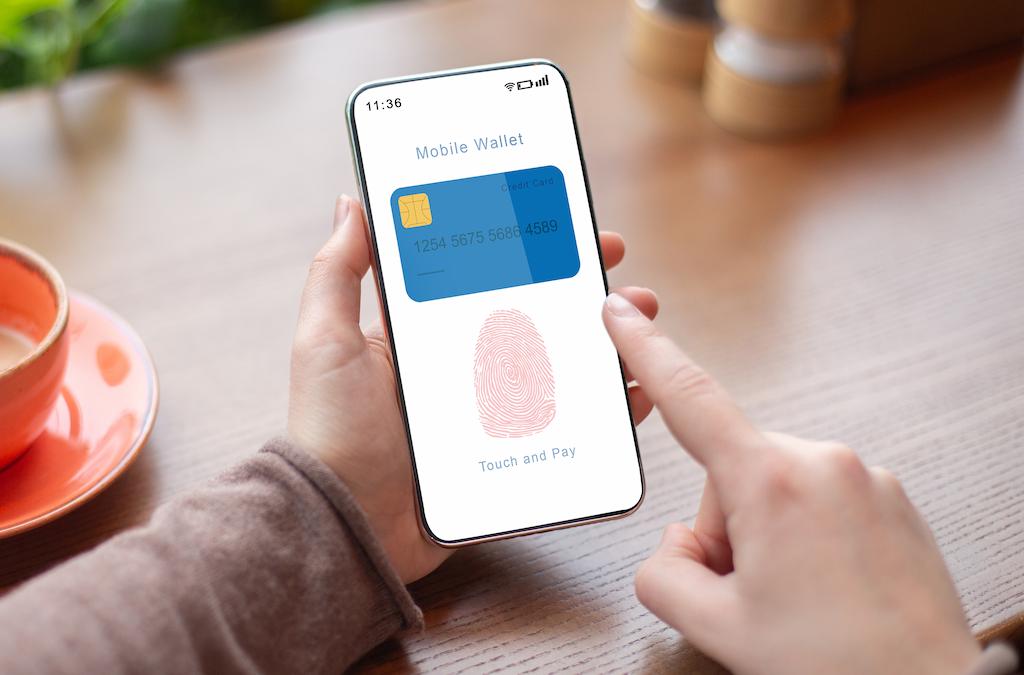
Mobile payments are one of the most secure forms of commerce due to the authentication methods used on mobile devices, such as facial recognition, fingerprints, and passcodes, as well as the encryption of transmissions.
This makes it very difficult for hackers to intercept customer data. In fact, mobile payment apps with face IDs (e.g., Apple Pay) are even more secure than EMV chip card payments.
Popularity
By 2025, mobile payments will overtake cash and card payments as they continue to grow at a steady rate of 26.63% per year. Convenience, additional security, and availability on a wide range of platforms are key adoption drivers of mobile payment technology.
Downsides of Mobile Payments
Mobile payments can be advantageous because they are convenient, fast, and secure. However, they can be costly and still vulnerable to technological failings.
- Peer-to-peer transactions: Refunds are nonexistent (or very hard to initiate). With no intermediary involved, it’s challenging to dispute charges after the fact. Human error – like sending money to the wrong recipient – can happen. Unpredictability is another downside;
- Specialized payment terminal: Mobile payment systems require a particular payment terminal because the payment process differs from a traditional point-of-sale terminal. For example, the terminal must accept wireless payments such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay;
- Device compatibility: A frustrating limitation of mobile payment apps is when they only work on one type of operating system, such as Apple Pay or Samsung. Additionally, some older devices may not have the necessary hardware components, such as NFC (Near Field Communication), to support mobile payment methods.
7 Top Mobile Payments Apps
From bank-level security to faster payments, these mobile payment apps help customers and merchants make payments in a snap.
1. Google Pay
Google Pay is a digital wallet and online payment system developed by Google to simplify payments and increase security. It uses NFC mobile payment technology to let users add cards and loyalty programs to their accounts, make payments in stores, apps, and websites, and send and request money from friends and family.
2. Cash App

Cash App is a mobile payment service developed by Square, Inc. It enables users to transfer money, purchase Bitcoin, buy and sell stocks, and receive direct deposits into their Cash App balance. It also provides a Cash Card, a debit card to make purchases with their Cash App balance.
3. PayPal
PayPal is an online payment platform that allows users to send and receive money, make online purchases, and transfer funds securely. It is widely used as an alternative to traditional banking services, as it is fast, secure, and convenient.
4. Zelle
Zelle is a free mobile app compatible with iOS and Android devices. Users can send money to friends and family by entering their phone numbers or email address, and payments can be made and received directly from a bank account.
5. Apple Pay
Apple Pay is a digital payment service created by Apple Inc. that allows customers to make payments in stores, in apps, and on the web with their Apple devices. It stores credit and debit card information and uses near-field communication (NFC) technology and one-time payment tokens to conduct secure payments.
6. Samsung Pay
Samsung Pay is a mobile payment and digital wallet service by Samsung Electronics that lets users make payments using compatible phones and other Samsung-produced devices. Samsung Pay uses near-field communication (NFC) and secure magnetic transmission (MST) to make secure payments.
7. Venmo
Venmo is a mobile app and website owned by PayPal, Inc. It lets users easily send and receive payments from friends, family, and other contacts. Venmo can be used for peer-to-peer payments, such as splitting restaurant bills or goods and services.
The Future of Mobile Payments System

In the future, mobile payment systems will be the norm. We predict the following trends:
- Super-apps: These provide users with digital services, such as financial services, that meet all their customers’ needs. Alipay and WeChat, two Chinese apps, are leading the charge and have a combined user base of over a billion people;
- Crypto payments: Bitcoin has already revolutionized mobile payments, and this trend will continue. Cryptocurrencies have empowered people with smartphones and internet connections to pay users worldwide;
- Buy now, pay later (BNPL): BNPL mobile payments solutions let customers spread out the total cost of their order over months or years. This flexibility in payment options benefits merchants, increasing their conversion rates and average order values.
Final Thoughts
As mobile payments continue to become more widespread, seeing how they shape the future of payments and commerce will be interesting. With the right strategies and infrastructure in place, mobile payments can provide an effective way for your business to make payments and transfer funds.
Trust E-Complish is your go-to leader in the Mobile Payments industry since 1998. Our expertise is unmatched, and MobilePay takes our service to the next level.
Our team will work with you to create a MobilePay solution that meets your business needs. Schedule a consultation or call toll-free at 888-847-7744 to learn to future-proof your business payment solutions.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents

