Table of Contents
Updated by 11.14.2023
Money Matters Made Safe: Top 10 Practices for Secure Online Payment Processing
Retailers lose more than $100 billion per year due to fraud, and by 2030, payment card fraud losses are destined to hit $49 billion. While big corporations may not feel the blow as much, many smaller businesses can’t afford such setbacks.
Enterprise size aside, no business should fall victim to payment processing fraud. While there will always be bad actors out there, several strategies and software capabilities are available to ensure secure online payment methods.
Let’s take a look at how you can improve online payment security methods for your business.
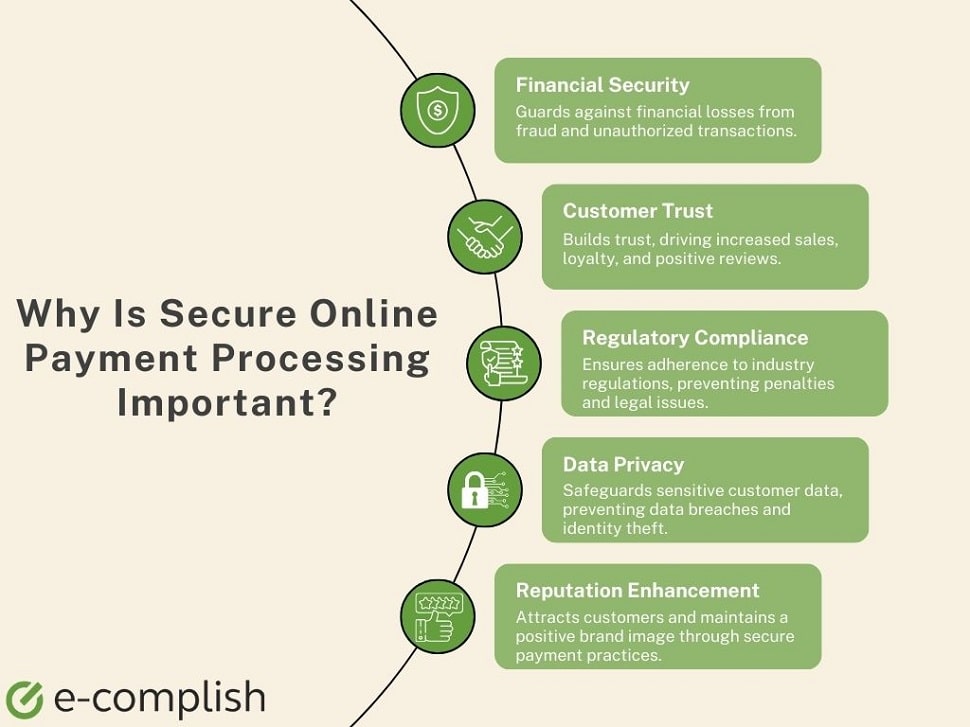
Why Is Secure Payment Processing Important?
Secure online payment processing has numerous benefits, such as reducing fraud, increasing customer trust, and ensuring compliance with regulations.
Most industry regulations also demand the use of secure payment methods. Hence, having a secure online payment processing system ensures you remain compliant and avoid potential legal repercussions.
10 Must-Have Practices for Ensuring Secure Payment Processing
1. Use Trusted Payment Gateways
A payment gateway software application lets you securely accept and process online or in-store payments. It reads, encrypts, and transmits data from credit cards, online wallets, and other applications to authorize transactions, acting as a middleman between merchants, customers, and financial institutions.
Without a payment gateway, you’d have to handle sensitive payment information, which requires complex and expensive measures. Many businesses use PayPal, Stripe, Square, and Amazon Pay as trusted payment gateways. This software integrates easily into eCommerce platforms and websites, offering secure payment transactions to enterprises of all sizes.
2. Implement SSL Encryption
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer – a security protocol that creates an encrypted link between a web server and a browser. It’s a digital certificate that authenticates a website’s identity and enables a secure connection.
Websites with SSL certificates display a padlock icon and a secure connection indicator, which instills trust in users, especially for eCommerce platforms. Not only does Google give preference to websites with SSL certificates when ranking them, but many industries, such as finance and healthcare, require SSL certificates to comply with data security regulations.
Nowadays, it’s also common to use transport layer security (TSL), which is SSL’s successor.
How to Get an SSL Certificate:
- Choose a certificate authority (CA): Some popular options include Let:s Encrypt, Namecheap, and Digicert.
- Generate a certificate signing request (CSR): This is a unique code your web server generates. You can use a CSR generator.
- Submit your CSR to the CA: They will verify your information and issue your SSL certificate.
- Install the certificate on your web server: The specific steps vary depending on your server type.
3. Embrace Tokenization
Tokenization is a security measure that safeguards confidential customer data, like credit card details, addresses, and account numbers. This process involves substituting such information with randomly generated symbols, preventing it from being easily obtained by unauthorized individuals.
As a result, data can be safely and securely transmitted through networks without compromising the privacy and security of customers’ personal information. Tokenization protects against fraudulent online transactions, reduces data breaches, and improves customer confidence.
It also simplifies the payment process as users do not have to enter their payment information repeatedly, and merchants do not need to store or maintain sensitive data, reducing liability and adhering to PCI compliance.
You must work with a payment processor or tokenization service provider (TSP) to get payment tokenization. Most payment processing facilities use tokenization as a standard security feature to protect customer data.
4. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
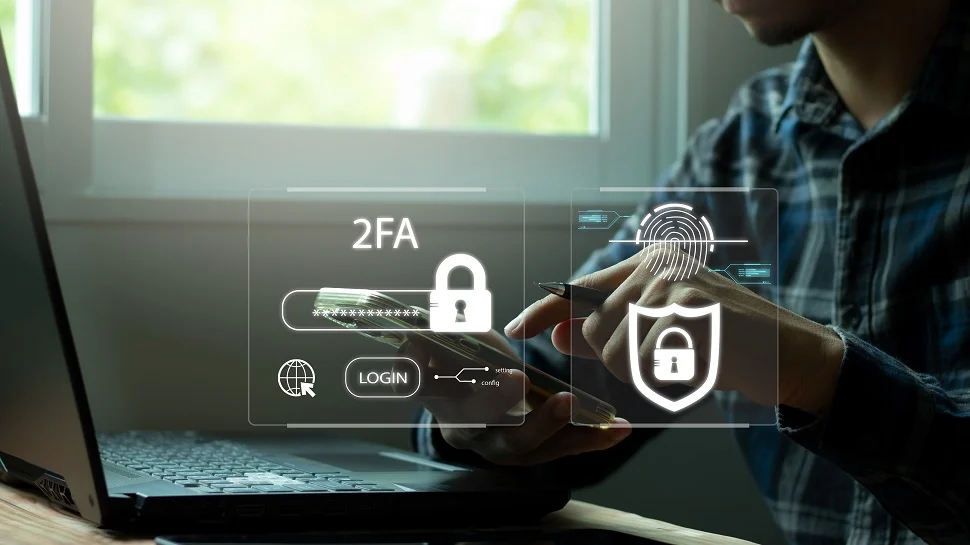

Two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly reduces unauthorized access to online accounts. It requires users to provide two forms of identification before accessing their accounts, such as a combination of a password, a PIN, or a fingerprint.
Banks often use 2FA, commonly through SMS codes, to increase security. This involves sending a unique code to a user’s phone to enter along with their regular login information.
Other methods include authentication apps, like Google Authenticator, and hardware tokens (physical devices), which generate unique codes upon button pressing. Hardware tokens are the most secure option as they are not internet-connected.
Commonly used authentication providers include Authy, Duo Security, and Okta. While not all payment processors offer 2FA authentication, many do provide this feature as an option. It is important to verify with your specific payment processor.
5. Regular Software Updates
A key aspect of maintaining a secure online payment processing system is regular software updates to patch vulnerabilities. Hackers are constantly finding new ways to exploit software weaknesses, but updates fix these weaknesses and prevent unauthorized access.
Prioritize critical software components such as operating systems, payment gateways, and antivirus software. Regular updates for operating systems (such as Windows, Mac OS, and Linux) are essential for keeping them secure and protected against the latest threats.
Payment gateways should also be regularly updated to avoid potential security breaches, which could result in the theft of sensitive customer data. Maintaining updated antivirus software is crucial for detecting and removing malicious software from systems. This provides an extra layer of protection against cybersecurity threats.
6. Ensure PCI DSS Compliance
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) is a collection of guidelines developed by prominent credit card companies like Visa, Mastercard, American Express, and Discover.
Its goal is to safeguard credit card information and establish uniform security measures. Adherence to PCI DSS is mandatory for all businesses that handle credit card data, including accepting, processing, storing, or transmitting it.
Some practical steps and guidance on how businesses can ensure PCI DSS compliance:
- Develop and implement security policies and procedures, including data, network, and physical security.
- Conduct annual PCI DSS assessments to identify and address security vulnerabilities in your systems and environment.
- Use strong passwords and encryption.
- Regularly update security software and applications to protect your systems from the latest security threats.
- Restrict employee access to sensitive data.
- Monitor your systems and networks for suspicious activity.
A qualified security provider can help you assess your security posture and implement the necessary security controls to achieve PCI DSS compliance.
7. Monitor Transactions for Fraud

In some cases, when fraudulent transactions are not detected and stopped in a timely manner, it can lead to bankruptcy or significant financial damage to businesses. For individual consumers, fraudulent credit card payments can result in overdraft fees, damaged credit scores, and difficulties in obtaining credit in the future.
Monitoring transactions for fraud is crucial in secure online payment processing to protect against financial loss, maintain compliance, preserve customer trust, and enable timely detection and prevention.
You can use machine learning algorithms, transaction monitoring systems, AVS, and 3D Secure to identify and prevent fraudulent activities. Implementing best practices, such as defining monitoring rules, setting up alerts, and regularly reviewing and updating rules, helps to prevent fraud.
8. Secure Data Storage
There are several ways to implement encryption and access control to protect stored payment data.
Here are a few examples:
- Encrypt databases and file systems: Use encryption to encrypt databases and file systems where payment data is stored. This will help to protect payment data from unauthorized access, even if the database or file system is compromised.
- Use a payment gateway: A payment gateway is a third-party service that processes credit and debit card transactions. Payment gateways typically use encryption to protect payment data in transit and at rest.
- Use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication: Require employees to use strong passwords and multi-factor authentication to access systems where payment data is stored.
- Implement role-based access control (RBAC): implement RBAC to restrict access to payment data to authorized employee users.
9. Educate Your Customers
When customers are more informed, they are more likely to take the necessary precautions to protect themselves from cyber threats. This, in turn, leads to secure online transactions for all parties involved.
Educating customers also helps to create a sense of trust and confidence in the online marketplace, leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty. You can use email newsletters, blog posts, and website FAQs on security-related topics to inform your customers about the following:
- Recognizing phishing attempts
- Secure password practices
- Public Wi-Fi risks
- Checking for secure websites
- Reviewing purchase history
Customers who are aware of potential risks and security measures contribute to a more secure and trustworthy online marketplace.
10. Enforce Strong Password Policies

Effective password protection is crucial in safeguarding payment accounts from potential hackers. Avoid using easily predictable passwords, such as sequential numbers or personal information, as these can easily be identified and accessed.
A strong password should be at least eight characters long and include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Utilizing a password manager is highly recommended.
To mitigate potential cyber threats, you can also use multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires additional verification measures, such as unique codes sent to mobile devices, physical identities, or location checks.
Partner with E-Complish for Industry-Leading Payment Solutions!
E-Complish is your ideal partner for businesses looking to streamline their payment processes and stay at the forefront of industry standards. Our cutting-edge technology, dedicated customer support, and customizable solutions help clients achieve their payment goals and stay competitive.
Our commitment to security, efficiency, and innovation makes us a reliable and trusted partner for all your online payment security needs. So why wait? Contact us today and experience industry-leading payment solutions that will take your business to new heights!
FAQs
Why is secure online payment processing important?
Why is secure online payment processing important?
Are these best practices applicable to mobile payment processing?
Table of Contents


